Portal:Africa



Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surface area. With nearly 1.4 billion people as of 2021, it accounts for about 18% of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest among all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Based on 2024 projections, Africa's population will exceed 3.8 billion people by 2100. Africa is the least wealthy inhabited continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, ahead of Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, corruption, colonialism, the Cold War, and neocolonialism. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and a large and young population make Africa an important economic market in the broader global context, and Africa has a large quantity of natural resources.
Africa is highly biodiverse; it is the continent with the largest number of megafauna species, as it was least affected by the extinction of the Pleistocene megafauna. However, Africa is also heavily affected by a wide range of environmental issues, including desertification, deforestation, water scarcity, and pollution. These entrenched environmental concerns are expected to worsen as climate change impacts Africa. The UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has identified Africa as the continent most vulnerable to climate change.
The history of Africa is long, complex, and varied, and has often been under-appreciated by the global historical community. In African societies the oral word is revered, and they have generally recorded their history via oral tradition, which has led anthropologists to term them "oral civilisations", contrasted with "literate civilisations" which pride the written word. African culture is rich and diverse both within and between the continent's regions, encompassing art, cuisine, music and dance, religion, and dress.
Africa, particularly Eastern Africa, is widely accepted to be the place of origin of humans and the Hominidae clade, also known as the great apes. The earliest hominids and their ancestors have been dated to around 7 million years ago, and Homo sapiens (modern human) are believed to have originated in Africa 350,000 to 260,000 years ago. In the 4th and 3rd millennia BCE Ancient Egypt, Kerma, Punt, and the Tichitt Tradition emerged in North, East and West Africa, while from 3000 BCE to 500 CE the Bantu expansion swept from modern-day Cameroon through Central, East, and Southern Africa, displacing or absorbing groups such as the Khoisan and Pygmies. Some African empires include Wagadu, Mali, Songhai, Sokoto, Ife, Benin, Asante, the Fatimids, Almoravids, Almohads, Ayyubids, Mamluks, Kongo, Mwene Muji, Luba, Lunda, Kitara, Aksum, Ethiopia, Adal, Ajuran, Kilwa, Sakalava, Imerina, Maravi, Mutapa, Rozvi, Mthwakazi, and Zulu. Despite the predominance of states, many societies were heterarchical and stateless. Slave trades created various diasporas, especially in the Americas. From the late 19th century to early 20th century, driven by the Second Industrial Revolution, most of Africa was rapidly conquered and colonised by European nations, save for Ethiopia and Liberia. European rule had significant impacts on Africa's societies, and colonies were maintained for the purpose of economic exploitation and extraction of natural resources. Most present states emerged from a process of decolonisation following World War II, and established the Organisation of African Unity in 1963, the predecessor to the African Union. The nascent countries decided to keep their colonial borders, with traditional power structures used in governance to varying degrees. (Full article...)
Selected article –
Thimlich Ohinga is a complex of stone-built ruins in Migori county, Nyanza Kenya, in East Africa. It is the largest one of 138 sites containing 521 stone structures that were built around the Lake Victoria region in Kenya. These sites are highly clustered. The main enclosure of Thimlich Ohinga has walls that are 1–3 m (3.3–9.8 ft) in thickness, and 1–4.2 m (3.3–13.8 ft) in height. The structures were built from undressed blocks, rocks, and stones set in place without mortar. The densely packed stones interlock. The site is believed to date to the 15th century or earlier. (Full article...)
Featured pictures –
Did you know (auto-generated) -

- ... that on February 3, 1986, African Independence Party leaders Adama Touré and Adama Touré were released from detention?
- ... that Ruth L. Bennett provided shelter for more than 2,000 black women and girls who migrated north to Chester, Pennsylvania, as part of the Great Migration?
- ... that South African president Jacob Zuma requested a tour of a Sainsbury's supermarket during his state visit to the United Kingdom in 2010?
- ... that scientists tested the age of an African termite's inhabited mound—and found it to be 34,000 years old?
- ... that Carver Court in Coatesville, Pennsylvania, was built to house African-American steelworkers during World War II?
- ... that the catalogue for Tanzania. Masterworks of African Sculpture highlighted traditional artworks such as a Sukuma mask?
Categories
Selected biography –
Chief Funmilayo Ransome-Kuti, MON (/fʊnmi ˈlaɪjoʊ ˈrænsəm ˈkuːti/; born Frances Abigail Olufunmilayo Olufela Folorunso Thomas; 25 October 1900 – 13 April 1978), also known as Funmilayo Aníkúlápó-Kuti, was a Nigerian educator, political campaigner, suffragist, and women's rights activist.
Fumilayo Ransome Kuti was born in Abeokuta, in what is now in Ogun State, and was the first female student to attend the Abeokuta Grammar School. As a young adult, she worked as a teacher, organizing some of the first preschool classes in the country and arranging literacy classes for lower-income women. (Full article...)
Selected country –
 |
 |
|
| ||
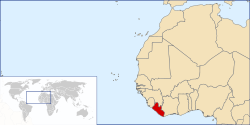
Liberia, officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the west coast of Africa, bordered by Sierra Leone, Guinea, and Côte d'Ivoire. Liberia, which means "Land of the Free", was founded as an independent nation, with support of the American government, for free-born and formerly enslaved Blacks and, thus, is one of only two nations in Africa (along with Ethiopia) that didn't fall under European domination. Since 1989, it has witnessed two civil wars, the First Liberian Civil War (1989 – 1996), and the Second Liberian Civil War (1999 – 2003), that have displaced hundreds of thousands of people and destroyed the country's economy.
The population of over 3 million comprises 16 indigenous ethnic groups and various foreign minorities. Indigenous peoples comprise about 95% of the population, the largest of which are the Kpelle in central and western Liberia. Americo-Liberians, who are descendants of freed slaves that arrived after 1821, make up an estimated 5% of the population. As of 2006, Liberia has the highest population growth rate in the world (4.91%). (Read more...)
Selected city –
Addis Ababa (/ˌædɪs ˈæbəbə/; Amharic: አዲስ አበባ, lit. 'new flower' [adˈdis ˈaβəβa] ⓘ ,Oromo: Finfinnee, lit. 'fountain of hot mineral water') is the capital city of Ethiopia, as well as the regional state of Oromia. With an estimated population of 2,739,551 inhabitants as of the 2007 census, it is the largest city in the country and the eleventh-largest in Africa. Addis Ababa is a highly developed and important cultural, artistic, financial and administrative center of Ethiopia. It is widely known as one of Africa's major capitals.
The founding history of Addis Ababa dates back to the late 19th century by Menelik II, Negus of Shewa, in 1886 after finding Mount Entoto unpleasant two years prior. At the time, the city was a resort town; its large mineral spring abundance attracted nobilities of the empire and led them to establish permanent settlement. It also attracted many members of the working classes – including artisans and merchants – and foreign visitors. Menelik II then formed his imperial palace in 1887. Addis Ababa became the empire's capital in 1889, and subsequently international embassies were opened. Urban development began with the 20th century, without any prior planning. (Full article...)
In the news
- 1 May 2025 –
- The bodies of three South African police officers who had been missing for six days are found in the Hennops River. (BBC News)
- Kenyan parliament member Charles Ong'ondo is shot to death in Nairobi by unknown gunmen on a motorcycle in an apparent assassination. (BBC News)
- 30 April 2025 – Puntland–Somaliland dispute
- Las Anod conflict, Puntland–Somaliland prisoner exchange
- Puntland releases fifteen prisoners of war in exchange for Somaliland releasing eleven combatants captured during the conflict in the contested Sool region. This is the second prisoner exchange of prisoners captured during the conflict in Las Anod. (Hiiraan Online) (Horn Observer)
- 30 April 2025 – Foreign relations of Taiwan, Somaliland–Taiwan relations
- Amid strengthening ties between Taiwan and Somaliland, the Somali government bans Taiwanese passport holders from Somalia, citing UN Resolution 2758 and the One China policy. Taiwan lodges a protest with Somalia and claims China instigated the ban. (BBC News) (Reuters)
- 29 April 2025 – Boko Haram insurgency
- At least 26 people are killed when a truck hits a roadside bomb in Borno State, Nigeria. (Al Jazeera)
Updated: 13:05, 3 May 2025
General images -
Africa topics
More did you know –

- ...that the 1459 Fra Mauro map (pictured) reports that "a junk from India" rounded the Cape of Good Hope in 1420, around 70 years before the navigations of Vasco da Gama?
- ...that the 1998 Sudan famine was caused by human rights abuses in the midst of the Second Sudanese Civil War?
- ...that a smokie is a West African delicacy made by blowtorching the carcass of a sheep or goat without removing its fleece?
- ...that Anne-Marie Nzié, a Cameroonian bikutsi singer, dedicated the song Liberté to President Paul Biya and his party, the Cameroon People's Democratic Movement?
Related portals
Major Religions in Africa
North Africa
West Africa
Central Africa
East Africa
Southern Africa
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus